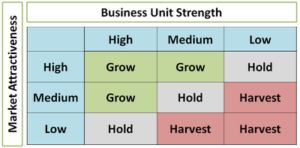
Large organizations with multiple business units need a way to determine where to invest across all the units. The GE–McKinsey Nine-Box Matrix is a method for deciding how to share capital across multiple units by assessing each unit’s market position and profitability.
This model looks at two factors: Market attractiveness and Business strength:
Market Attractiveness is rated according to market size, market growth rate, historical profit margins, level of competition and similar criteria
Business Strength is rated according market share, market share growth, product quality, brand strength and similar criteria
Organizations determine their criterion and may apply different weighting factor to each criteria. The matrix may look something like this:
Based on the business unit’s position in the matrix, leaders decide how to invest. Those at the top left of the matrix have a high market attractiveness and strong business strength and should be grown. Those in-between have a medium rating and may warrant a selective investment. Those at the bottom right have low scores and should be harvested for cash, manage for earnings or divest.